How to Identify Cyber Security Threats [Top 10 Security Threats]
Key Takeaways
- The most prevalent cyber threats include malware variants, phishing (including spear and whaling), man‑in‑the‑middle, ransomware, DDoS, IoT attacks, data breaches and mobile‑app malware.
- Phishing is involved in over 90 % of incidents.
- Applying the CIS Critical Security Controls, especially inventory of hardware and software, continuous vulnerability management, privileged‑access control, and secure configuration, can eliminate 80‑95 % of known vulnerabilities.
- Core defense tactics are regular patching, ongoing phishing awareness training with simulated attacks, and strict privilege management to limit malware impact.
In the wake of the recent cyber attacks that hit three school districts in Louisiana, the issue of cyber crime is once again at the forefront of our minds. Questions regarding how to identify cyber security threats are at an all-time high.
There are several types of cyber threats, as well as varying motives of the attackers. While some cyber criminals are in it for financial gain, others are motivated by disruption or espionage.
Regardless of the motive, the top 10 cyber security threats (and subsequent cyber threats definitions) include:
Types of Cyber Threats
- Malware — A combination of the words "malicious" and "software", malware is a type of cyber threat designed to harm a computer, system, or data. Examples include adware, ransomware, scareware, spyware, Trojans, viruses, and worms.
- Phishing — Phishing is a specific threat in cyber security wherein cyber criminals send phony emails (often employing social engineering) that entice users to click a link or respond to data in the hopes of stealing a user's sensitive information.
- Spear phishing — Spear phishing is simply a targeted phishing attack, such as an attack on corporate executives (also known as "whaling") or government officials.
- Man-in-the-middle attack — A MITM attack is when an attacker intercepts communications between two parties for the purpose of stealing information, spying, corrupting data, or sabotaging communication.
- Trojans — A type of malware, the Trojan virus is often disguised as legitimate software for the purpose of gaining access to a user's system.
- Ransomware — Ransomware is a type of malware designed to deny access to a computer system or data until a specified ransom is paid.
- Denial of Service Attack or Distributed Denial of Service Attack (DDoS) — A DDoS attack happens when multiple compromised computer systems attack a target, such as a server, website, or network, resulting in a denial of service.
- Attacks on IoT devices — IoT (Internet of Things) connects devices via the internet, and hackers can exploit internet connectivity to steal data.
- Data breaches — A data breach is a security incident in which information is accessed illegally.
- Malware on mobile apps — The majority of mobile attacks come from malware or malicious wifi.
Cyber Security Statistics
The Verizon Data Breach Investigations Report (DBIR) is one of the most respected annual reports in the security industry. Every year, one of the largest IT investigative entities in the world (the Verizon Research, Investigations, Solutions and Knowledge team) shares research into the state of cybersecurity for the year, including the largest trends.
In 2017, the team found that:
- Phishing is used in more than 90 percent of security incidents and breaches.
- 30 percent of phishing messages were opened in 2016—up from 23 percent the year before—and in 12 percent of those events, users clicked to open the malicious attachment or link.
The Verizon 2016 DBIR highlights the rise of a three-pronged phishing attack:
- The user receives a phishing email with a malicious attachment or a link pointing to a malicious website.
- The user downloads malware, which attackers can use to look for secrets and internal information, steal credentials to multiple applications through key logging, or encrypt files for ransom.
- Attackers can also use stolen credentials for further attacks: for example, to log into third-party websites like banking or retail sites.
Take Security to the Next Level Rapidly with the CSC Top 5
Research and case studies from the CIS show that configuring IT systems in compliance with CIS benchmarks can eliminate 80 to 95 percent of known security vulnerabilities. In particular, the Top 5 CIS Critical Security Controls establish a solid foundation for radically improving an organization’s security posture.
1. Inventory and Control of Hardware Assets
As per the CIS itself: “Actively manage (inventory, track, and correct) all hardware devices on the network so that only authorized devices are given access, and unauthorized and unmanaged devices are found and prevented from gaining access.”
2. Inventory and Control of Software Assets
As above, but for software: “Actively manage (inventory, track, and correct) all software on the network so that only authorized software is installed and can execute, and that unauthorized and unmanaged software is found and prevented from installation or execution.”
3. Continuous Vulnerability Management
“Continuously acquire, assess, and take action on new information in order to identify vulnerabilities, remediate, and minimize the window of opportunity for attackers.”
4. Controlled Use of Administrative Privileges
“The misuse of administrative privileges is a primary method for attackers to spread inside a target enterprise.” Provide processes and tools “to track/control/prevent/correct the use, assignment, and configuration of administrative privileges on computers, networks, and applications.”
5. Secure Configuration for Hardware and Software
“Establish, implement, and actively manage (track, report on, correct) the security configuration of laptops, servers, and workstations using a rigorous configuration management and change control process in order to prevent attackers from exploiting vulnerable services and settings. (As delivered by manufacturers and resellers, the default configurations for operating systems and applications are normally geared towards ease-ofdeployment and ease-of-use—not security.)”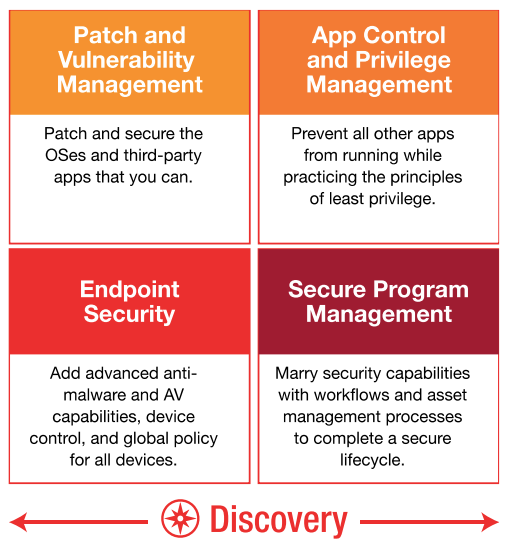
Ivanti's Defense-in-Depth Solutions
The takeaway is this: with each business-critical asset in your organization, you should compare your existing security controls against the CIS Critical Security Controls. Pinpoint exactly which sub-controls within those you already meet and those you do not. Then, based on identified gaps and specific business risks and concerns, take immediate steps to implement the Top 5 Controls and develop a strategic plan to implement the others.
We can help. Ivanti provides a comprehensive, targeted portfolio that addresses the Top 5 and other CSC controls, aligning IT Operations and Security to best meet customer cybersecurity needs.
Automated capabilities such as discovery, patch management, application and device control, administrative privilege management, and secure configuration—essential elements of the Top 5 CIS Controls—power Ivanti solutions. What’s more, Ivanti helps customers implement those Controls successfully, economically, and easily, with minimal impact on user productivity. Users don’t need to call the service desk every five minutes for access rights. Unauthorized, insecure, “shadow IT” workarounds are eliminated. Business still gets done at speed.
Ivanti CISO Phil Richards outlined three critical defense tactics that organizations should employ to help prevent and/or mitigate the fallout of a cyber attack:
- Patching: As the first line of defense, consistent patching ensures that operating systems and third-party applications are up to date.
- User Education on Phishing/Spam Emails: As phishing emails get more advanced, so should a company's security training. For example, regular phishing email drills that provide immediate feedback when users click a link.
- Privilege Management: Minimizing privileges is an important tactic to mitigate the damage caused by many types of malware, including ransomware.


